3. Packages
Archive Packages
An Archive Package is a digital container for data, functioning technically as a directory for files. It is always associated with its parent archive and can only be controlled or accessed by a Data Responsible. The use of Archive Packages involves several key steps and prerequisites, as outlined below.
Prerequisites
The use of Archive Packages requires the following:
- Role: Data Responsible
- Accepted Project
- SSH Public Key
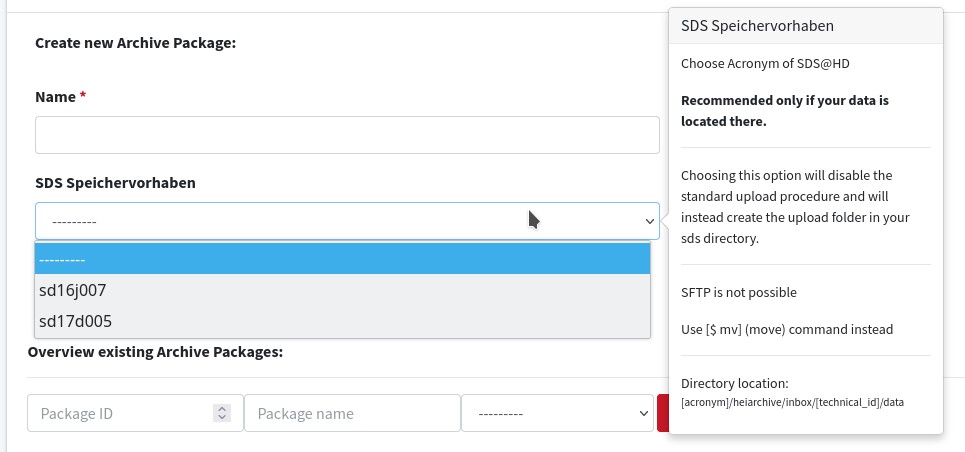
1. Creation of Archive Packages
For SDS@hd users, the relevant SV can be selected. Available SVs are populated at login. Selecting this option modifies how data must be provided to heiARCHIVE. Users must enter a name for the Archive Package for identification purposes and then press 'Create Package'.

Package Information
Package information is continuously updated, with further details available for every process stage. Such information includes downloadable metadata files such as a tree abstraction of the package (filelist.txt) - available after the Inbox stage, and manifest files (checksums for each file) - available after Ingest.
2. Data Upload
When the connection to the package is available, data can be uploaded by connecting to the Archive Package using SFTP. The SFTP connection schema is
3. Metadata Provision
Metadata plays a crucial role in describing data stored in long-term archives. It provides essential information about the content, context, and structure of the archived data, enabling efficient discovery, retrieval, and interpretation in the future. In the realm of long-term archiving, adhering to standardized metadata formats is paramount for interoperability and preservation purposes.
One widely recognized standard for metadata in the research community is the "DataCite Standard". This standard offers a comprehensive framework for describing research data and ensuring its long-term accessibility and discoverability. By adopting the DataCite Standard, we leverage its numerous advantages in managing our archived data.
The DataCite Standard provides a consistent and structured approach to capturing metadata, facilitating data citation, reproducibility, and proper attribution. It enables researchers to cite and reference archived datasets effectively, enhancing scholarly communication and supporting collaboration across various disciplines. Additionally, the standard supports the discovery of research data by providing rich descriptive information that aids in data search and retrieval.
For our archival packages stored in heiARCHIVE, we have selected the following items from the DataCite Standard to describe our datasets. These items encompass crucial metadata elements that ensure comprehensive documentation of the archived packages:
Mandatory fields:
- title (free text)
- ressource type (free text)
- ressource type general (choose from list: dataset, collection, ...)
- subjects (scientific field according to DFG classification)
- creators (at least one of the following)
- personal creators (given name / family name / optional: orcid ID)
- organizational creators (name)
Optional fields:
- description (free text)
- language
- related identifiers (e.g. DOIs)
- license (e.g. CC-BY-4.0)
- funders (funder + award number)
By incorporating these selected items from the DataCite Standard, we ensure that our archived packages in heiARCHIVE are well-described, enabling future users to understand, locate, and utilize the data effectively.
But DataCite represents merely a list of core metadata properties. Notably, it does not include comprehensive, subject-specific information. Therefore, it is advised to store additional metadata (for instance, in subject-specific schemas) and/or extended documentation and descriptions along with the data.
4. Starting Archiving
The archiving process is the final step and irreversible once initiated. Upon providing metadata and activating the process, the data as is in the Archive Package is stored on various backends. HeiARCHIVE will then calculate a checksum and the size (SI-Metric) of the uploaded data. Users will be notified via notifications and email about the updates on their Archive Package, including the success or failure of the archiving process.
